Endocannabinoid system
This system is central to many core functions in our body and can uniquely receive the CBN, THC, & CBD molecules found in cannabis. The ECS is comprised of many different signaling molecules, receptors, and enzymes that impact our physiological processes.
The two most studied are the CB1 & CB2 receptors. These control pain modulation, appetite, memory, anti-inflammatory response, and other immune system responses. ECS receptors are found on cell surfaces and although they are present in everyone, each body is different, which is why a wide range of reactions to these cannabinoids occur.
CB1
These receptors are concentrated in the brain, central nervous system and scattered throughout other bodily tissue.
CB2
Found in peripheral organs and cells associated with the immune system throughout the body. The highest concentration of these receptors is in the gut.
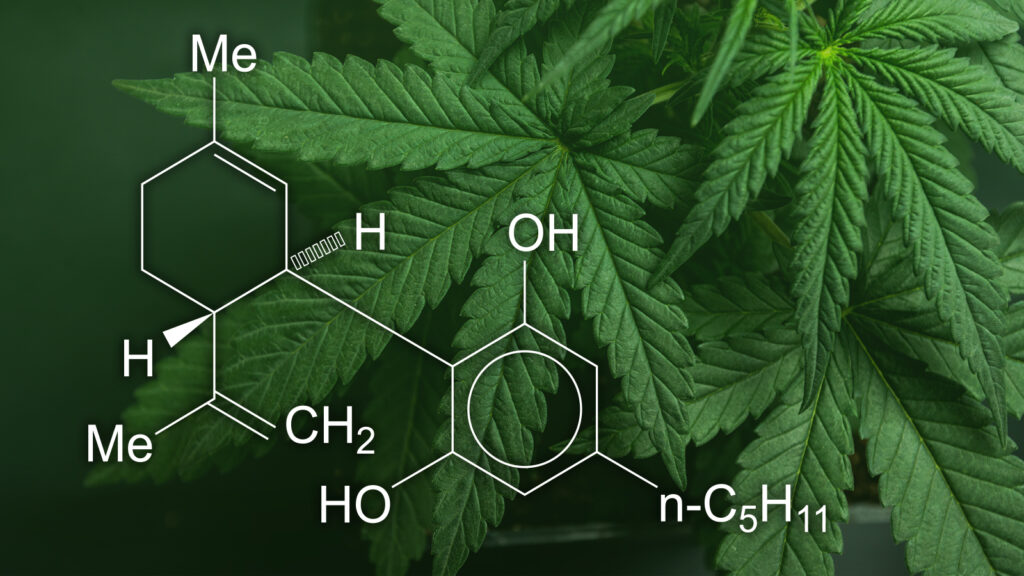
Cannabinoids
Phytocannabinoids are found in the cannabis plant and are what make each strain completely unique. Surprisingly enough these compounds are also produced by our bodies: these are known as endocannabinoids. When Phytocannabinoids are ingested by mammals, they are accepted by our endocannabinoid receptors, and produce a physical response that can have therapeutic effects.
Entourage effect
This is when different cannabis compounds interact synergisticly to magnify the therapeutic benefits of a single compound. Simply put, the medicinal benefits of a whole plant (with its variety of terpenes and cannabinoids) are greater than a single isolated compound.